The difference between quartz stone and barite
 April.07,2024
April.07,2024

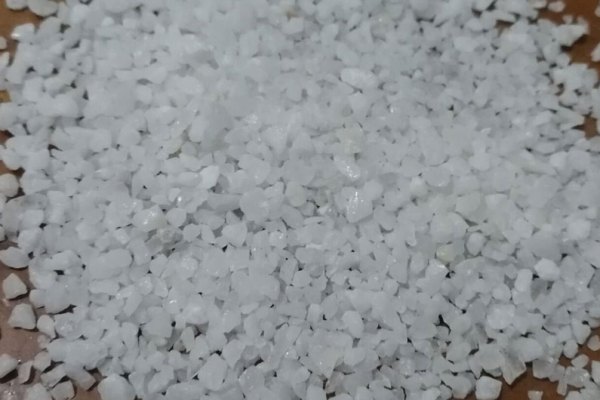
The main chemical composition of quartz is SiO2. Pure quartz crystal is colorless and transparent, but it often displays different colors due to inclusions and trace elements, usually milky white, colorless, gray; glass luster, and fracture grease luster. Specific gravity: 2.22~2.65; Mohs hardness: 7.0; PH’: 6.0; melting point: 1750°C; piezoelectric.
Quartz is widely used in glass, casting, ceramics and refractory materials, metallurgy, construction, chemicals, plastics, rubber, abrasives, electronics, coatings, aerospace, jewelry and other industries.
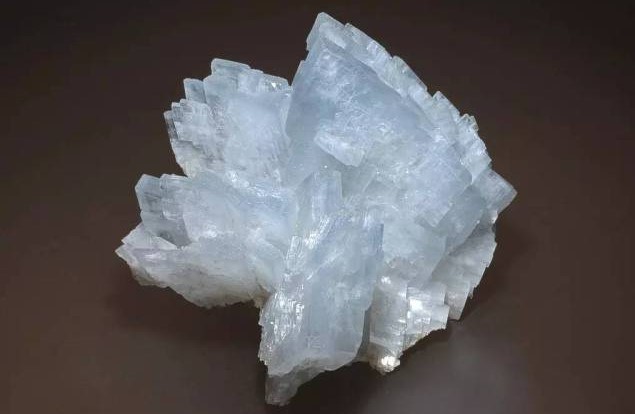
Barite is the most common mineral of barium, and its component is barium sulfate; the crystals of barite are large tube-shaped, and the crystals sometimes gather together to form rosette-shaped or bifurcated crystal blocks, which are called pappus. Barite. Pure barite is colorless and transparent, generally white, light yellow, or light brown with glass luster. Hardness: 3~3.5; specific gravity 4.3~4.5; melting point 1580℃.
Barite has a wide range of industrial uses. Barite powder can be used as drilling mud weighting agent, zinc-barium white pigment; filler in the paint, papermaking, rubber and plastic industries; mineralizer in the cement industry, radiation-proof mortar and concrete, refined kerosene, etc.; used for digestive tract imaging in the pharmaceutical industry agent; it can also be used to make pesticides, leather, fireworks, etc.





