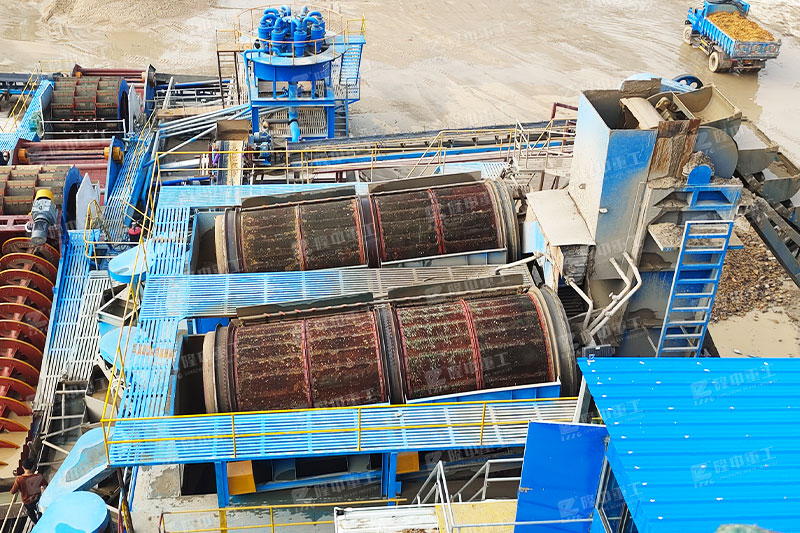
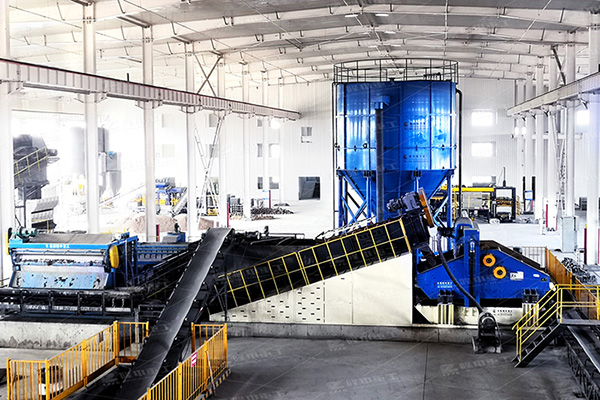
Jigging machines for tungsten tin and gold ore dressing
 July.21,2025
July.21,2025
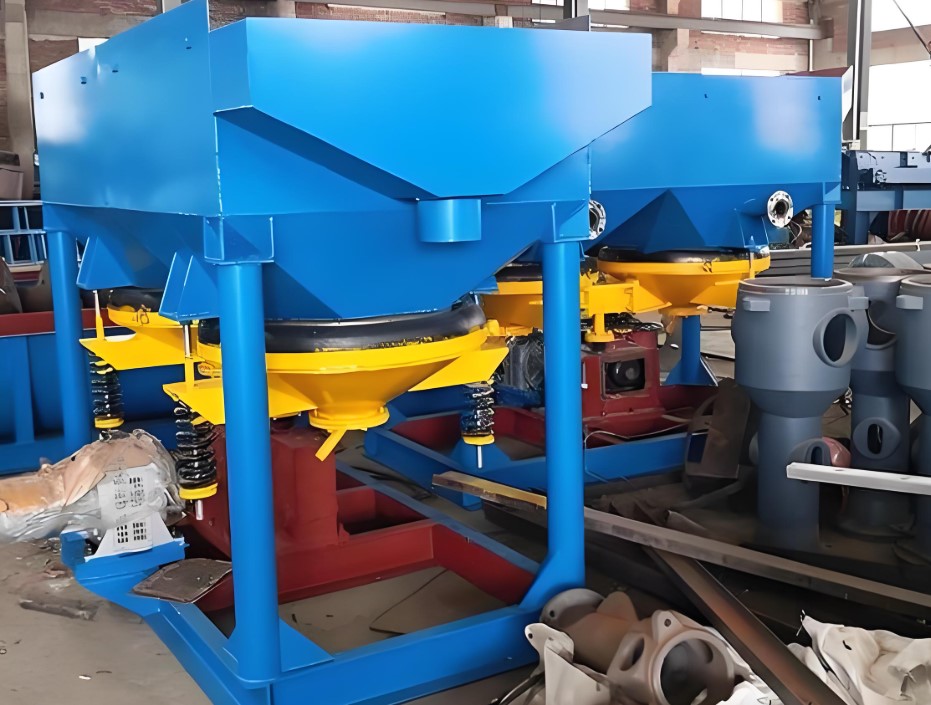

Metal beneficiation plants mostly use hydraulic jigging. Jigging is often used for the beneficiation of non-ferrous metal ores such as tungsten and tin and coal. Generally, the greater the relative density difference of the selected ore particles, the narrower the particle size range (the smaller the difference in particle size), and the better the sorting effect.
In coal sorting, jigging accounts for a large proportion. About 50% of the coal selected worldwide each year is processed by jigs; in my country, jigging accounts for 70% of the total raw coal selected. In addition, the particle size level of jigging coal selection is relatively wide, ranging from 150 to 0.5 mm; it can be selected without classification or by classification. Jigging coal selection has strong adaptability. Unless it is extremely difficult to select coal, jigging can be given priority.
In ore sorting, jigging is an effective method for processing coarse and medium-grained ores. It is widely used for sorting tungsten, tin, gold and some rare metal ores; in addition, it is also used for sorting iron, manganese and non-metallic ores. When processing metal ores, the upper limit of the feed particle size can reach 30~50mm, and the lower limit of the recovered particle size is 0.2~0.074mm.




